Standard Form
| Site: | Clare |
| Course: | Michigan Algebra I Sept. 2012 |
| Book: | Standard Form |
| Printed by: | Guest user |
| Date: | Tuesday, December 23, 2025, 4:28 PM |
Description
Standard Form
Introduction
Example 1 Find the a, b, and c values of the equation: x2 - 3x = 28.
Step 1. Put the equation in standard form.
1x2 - 3x - 28 = 0
Step 2. Identify the a, b, and c values.
a = 1, b = -3, c = -28
Example 2 Find the a, b, and c values of the equation: 5x2 = -45.
Step 1. Put the equation in standard form.
5x2 + 0x + 45 = 0
Step 2. Identify the a, b, and c values.
a = 5, b = 0, c = 45
Exploration Activity
Answer Key
Standard Form Exploration Activity Answer Key
Â
Guided Practice
Guided Practice
Practice
Answer Key
Standard to Vertex Form
Example Rewrite y = 3x2 - 6x + 7 in vertex form.
Step 1. Find the x-coordinate of the vertex.
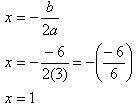
Step 2. Find the y-coordinate of the vertex.
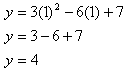
Step 3. Rewrite the equation in vertex form.
Completing the Square
Example Convert y = x2 + 4x - 7 to vertex form.
In this equation, a = 1.
![]()
Step 3. Add the constant that will create a perfect square trinomial to each side.
![]()
Step 4. Factor and simplify.
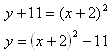
Practice
Answer Key
Sources
Coffman, Joseph. "Translating Parabolas." http://www.jcoffman.com/Algebra2/ch5_3.htm (accessed 07/25/2010).
Embracing Mathematics, Assessment & Technology in High Schools; A Michigan Mathematics & Science Partnership Grant Project
Holt, Rinehart & Winston, "Quadratic Functions and Equations ." http://my.hrw.com/math06_07/nsmedia/homework_help/alg1/alg1_ch09_03_homeworkhelp.html (accessed 8/22/2010).
Kuta Software, "Free Algebra 2 Worksheets." http://www.kutasoftware.com/freeia2.html (accessed 08/05/2010).